R语言实战:重抽样与自助法
目录
本文内容来自《R 语言实战》(R in Action, 2nd),有部分修改
置换检验
置换检验,随机化检验,重随机化检验
精确检验 vs 蒙特卡洛模拟
使用 coin 包做置换检验
- 响应值与组的分配独立吗?
- 两个数值变量独立吗?
- 两个类别型别变量独立吗?
library(coin)
独立两样本和 K 样本检验
score <- c(
40, 57, 45, 55, 58,
57, 64, 55, 62, 65
)
treatment <- factor(
c(rep("A", 5), rep("B", 5))
)
my_data <- data.frame(
treatment, score
)
my_data
treatment score
1 A 40
2 A 57
3 A 45
4 A 55
5 A 58
6 B 57
7 B 64
8 B 55
9 B 62
10 B 65
t 检验,结果显著
t.test(
score ~ treatment,
data=my_data,
var.equal=TRUE
)
Two Sample t-test
data: score by treatment
t = -2.345, df = 8, p-value = 0.04705
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-19.0405455 -0.1594545
sample estimates:
mean in group A mean in group B
51.0 60.6
置换检验,结果不显著
oneway_test(
score ~ treatment,
data=my_data,
distribution="exact"
)
Exact Two-Sample Fisher-Pitman Permutation Test
data: score by treatment (A, B)
Z = -1.9147, p-value = 0.07143
alternative hypothesis: true mu is not equal to 0
library(MASS)
UScrime <- transform(
UScrime,
So = factor(So)
)
head(UScrime)
M So Ed Po1 Po2 LF M.F Pop NW U1 U2 GDP Ineq Prob Time y
1 151 1 91 58 56 510 950 33 301 108 41 394 261 0.084602 26.2011 791
2 143 0 113 103 95 583 1012 13 102 96 36 557 194 0.029599 25.2999 1635
3 142 1 89 45 44 533 969 18 219 94 33 318 250 0.083401 24.3006 578
4 136 0 121 149 141 577 994 157 80 102 39 673 167 0.015801 29.9012 1969
5 141 0 121 109 101 591 985 18 30 91 20 578 174 0.041399 21.2998 1234
6 121 0 110 118 115 547 964 25 44 84 29 689 126 0.034201 20.9995 682
Wilcoxon 秩和检验
wilcox.test(
Prob ~ So,
data=UScrime,
)
Wilcoxon rank sum exact test
data: Prob by So
W = 81, p-value = 8.488e-05
alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
wilcox_test(
Prob ~ So,
data=UScrime,
distribution="exact"
)
Exact Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test
data: Prob by So (0, 1)
Z = -3.7493, p-value = 8.488e-05
alternative hypothesis: true mu is not equal to 0
近似 K 样本置换检验
library(multcomp)
head(cholesterol)
trt response
1 1time 3.8612
2 1time 10.3868
3 1time 5.9059
4 1time 3.0609
5 1time 7.7204
6 1time 2.7139
set.seed(1234)
oneway_test(
response ~ trt,
data=cholesterol,
distribution=approximate(nresample=9999)
)
Approximative K-Sample Fisher-Pitman Permutation Test
data: response by trt (1time, 2times, 4times, drugD, drugE)
chi-squared = 36.381, p-value < 1e-04
列联表中的独立性
chisq_test()、cmh_test()、lbl_test() 函数
library(vcd)
head(Arthritis)
ID Treatment Sex Age Improved
1 57 Treated Male 27 Some
2 46 Treated Male 29 None
3 77 Treated Male 30 None
4 17 Treated Male 32 Marked
5 36 Treated Male 46 Marked
6 23 Treated Male 58 Marked
Improved 是有序因子,进行线性趋势检验
set.seed(1234)
chisq_test(
Treatment ~ Improved,
data=Arthritis,
distribution=approximate(nresample=9999)
)
Approximative Linear-by-Linear Association Test
data: Treatment by Improved (None < Some < Marked)
Z = -3.6075, p-value = 0.0006001
alternative hypothesis: two.sided
Arthritis_v2 <- transform(
Arthritis,
Improved=as.factor(as.numeric(Improved))
)
head(Arthritis_v2)
ID Treatment Sex Age Improved
1 57 Treated Male 27 2
2 46 Treated Male 29 1
3 77 Treated Male 30 1
4 17 Treated Male 32 3
5 36 Treated Male 46 3
6 23 Treated Male 58 3
Improved 是分类因子,进行卡方检验
set.seed(1234)
chisq_test(
Treatment ~ Improved,
data=Arthritis_v2,
distribution=approximate(nresample=9999)
)
Approximative Pearson Chi-Squared Test
data: Treatment by Improved (1, 2, 3)
chi-squared = 13.055, p-value = 0.0018
数值变量间的独立性
spearman_test() 函数
states <- as.data.frame(state.x77)
head(states)
Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad Frost
Alabama 3615 3624 2.1 69.05 15.1 41.3 20
Alaska 365 6315 1.5 69.31 11.3 66.7 152
Arizona 2212 4530 1.8 70.55 7.8 58.1 15
Arkansas 2110 3378 1.9 70.66 10.1 39.9 65
California 21198 5114 1.1 71.71 10.3 62.6 20
Colorado 2541 4884 0.7 72.06 6.8 63.9 166
Area
Alabama 50708
Alaska 566432
Arizona 113417
Arkansas 51945
California 156361
Colorado 103766
set.seed(1234)
spearman_test(
Illiteracy ~ Murder,
data=states,
distribution=approximate(nresample=9999)
)
Approximative Spearman Correlation Test
data: Illiteracy by Murder
Z = 4.7065, p-value < 1e-04
alternative hypothesis: true rho is not equal to 0
两样本和 K 样本相关性检验
两配对组的置换检验:wilcoxsign_test() 函数
多于两组:friedman_test() 函数
Wilcoxon 符号秩检验
wilcoxsign_test(
U1 ~ U2,
data=UScrime,
distribution="exact"
)
Exact Wilcoxon-Pratt Signed-Rank Test
data: y by x (pos, neg)
stratified by block
Z = 5.9691, p-value = 1.421e-14
alternative hypothesis: true mu is not equal to 0
深入研究
independence_test() 函数
lmPerm 包的置换检验
线性模型的置换检验,比如 lmp() 和 aovp() 函数
library(lmPerm)
简单回归和多项式回归
set.seed(1234)
fit <- lmp(
weight ~ height,
data=women,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
summary(fit)
Call:
lmp(formula = weight ~ height, data = women, perm = "Prob")
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.7333 -1.1333 -0.3833 0.7417 3.1167
Coefficients:
Estimate Iter Pr(Prob)
height 3.45 5000 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.525 on 13 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-Squared: 0.991, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9903
F-statistic: 1433 on 1 and 13 DF, p-value: 1.091e-14
二次方程
set.seed(1234)
fit <- lmp(
weight ~ height + I(height^2),
data=women,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
summary(fit)
Call:
lmp(formula = weight ~ height + I(height^2), data = women, perm = "Prob")
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.509405 -0.296105 -0.009405 0.286151 0.597059
Coefficients:
Estimate Iter Pr(Prob)
height -7.34832 5000 <2e-16 ***
I(height^2) 0.08306 5000 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.3841 on 12 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-Squared: 0.9995, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9994
F-statistic: 1.139e+04 on 2 and 12 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
多元回归
head(states)
Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad Frost
Alabama 3615 3624 2.1 69.05 15.1 41.3 20
Alaska 365 6315 1.5 69.31 11.3 66.7 152
Arizona 2212 4530 1.8 70.55 7.8 58.1 15
Arkansas 2110 3378 1.9 70.66 10.1 39.9 65
California 21198 5114 1.1 71.71 10.3 62.6 20
Colorado 2541 4884 0.7 72.06 6.8 63.9 166
Area
Alabama 50708
Alaska 566432
Arizona 113417
Arkansas 51945
California 156361
Colorado 103766
fit <- lmp(
Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost,
data=states,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
summary(fit)
Call:
lmp(formula = Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost,
data = states, perm = "Prob")
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-4.79597 -1.64946 -0.08112 1.48150 7.62104
Coefficients:
Estimate Iter Pr(Prob)
Population 2.237e-04 51 1.000
Illiteracy 4.143e+00 5000 <2e-16 ***
Income 6.442e-05 51 0.961
Frost 5.813e-04 51 0.863
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 2.535 on 45 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-Squared: 0.567, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5285
F-statistic: 14.73 on 4 and 45 DF, p-value: 9.133e-08
fit <- lm(
Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost,
data=states,
)
summary(fit)
Call:
lm(formula = Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost,
data = states)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-4.7960 -1.6495 -0.0811 1.4815 7.6210
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 1.235e+00 3.866e+00 0.319 0.7510
Population 2.237e-04 9.052e-05 2.471 0.0173 *
Illiteracy 4.143e+00 8.744e-01 4.738 2.19e-05 ***
Income 6.442e-05 6.837e-04 0.094 0.9253
Frost 5.813e-04 1.005e-02 0.058 0.9541
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 2.535 on 45 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.567, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5285
F-statistic: 14.73 on 4 and 45 DF, p-value: 9.133e-08
注意:在 lm() 中 Population 和 Illiteracy 均显著,而 lmp() 中仅 Illiteracy 显著
单因素方差分析和协方差分析
单因素方差分析的置换检验
set.seed(1234)
fit <- aovp(
response ~ trt,
data=cholesterol,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS "
anova(fit)
Analysis of Variance Table
Response: response
Df R Sum Sq R Mean Sq Iter Pr(Prob)
trt 4 1351.37 337.84 5000 < 2.2e-16 ***
Residuals 45 468.75 10.42
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
单因素协方差分析的置换检验
set.seed(1234)
fit <- aovp(
weight ~ gesttime + dose,
data=litter,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
anova(fit)
Analysis of Variance Table
Response: weight
Df R Sum Sq R Mean Sq Iter Pr(Prob)
gesttime 1 161.49 161.493 5000 0.0006 ***
dose 3 137.12 45.708 5000 0.0392 *
Residuals 69 1151.27 16.685
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
双因素方差分析
set.seed(1234)
fit <- aovp(
len ~ supp*dose,
data=ToothGrowth,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
anova(fit)
Analysis of Variance Table
Response: len
Df R Sum Sq R Mean Sq Iter Pr(Prob)
supp 1 205.35 205.35 5000 < 2e-16 ***
dose 1 2224.30 2224.30 5000 < 2e-16 ***
supp:dose 1 88.92 88.92 2032 0.04724 *
Residuals 56 933.63 16.67
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
双因素方差分析
set.seed(1234)
fit <- aovp(
len ~ supp*dose,
data=ToothGrowth,
perm="Prob"
)
[1] "Settings: unique SS : numeric variables centered"
anova(fit)
Analysis of Variance Table
Response: len
Df R Sum Sq R Mean Sq Iter Pr(Prob)
supp 1 205.35 205.35 5000 < 2e-16 ***
dose 1 2224.30 2224.30 5000 < 2e-16 ***
supp:dose 1 88.92 88.92 2032 0.04724 *
Residuals 56 933.63 16.67
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
置换检验点评
perm 包
corrperm 包
logregperm 包
glmperm 包
置换检验主要用于生成检验零假设的 p 值,有助于回答“效应是否存在”这样的问题。
自助法
从初始样本重复随机替换抽样,生成一个或一系列待检验统计量的经验分布。 无需假设一个特定的理论分布,便可生成统计量的置信区间,并能检验统计假设。
boot 包中的自助法
library("boot")
对单个统计量使用自助法
计算 R 平方的函数
rsq <- function(formula, data, indices) {
d <- data[indices,]
fit <- lm(formula, data=d)
return (summary(fit)$r.square)
}
自助抽样
set.seed(1234)
results <- boot(
data=mtcars,
statistic=rsq,
R=1000,
formula=mpg ~ wt + disp
)
boot 对象可以输出
print(results)
ORDINARY NONPARAMETRIC BOOTSTRAP
Call:
boot(data = mtcars, statistic = rsq, R = 1000, formula = mpg ~
wt + disp)
Bootstrap Statistics :
original bias std. error
t1* 0.7809306 0.01379126 0.05113904
绘制结果
plot(results)
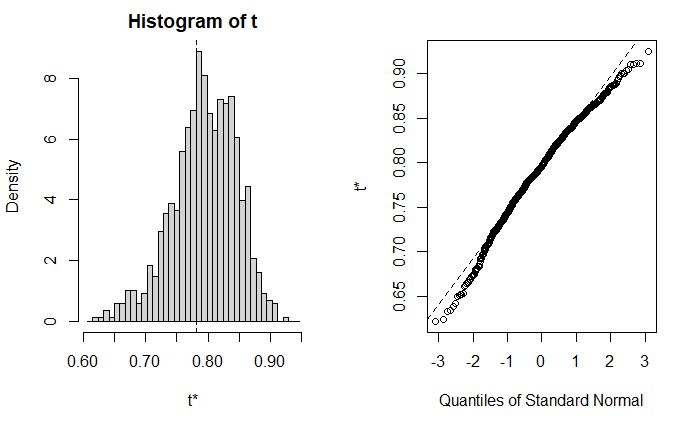
计算置信区间
ci_results <- boot.ci(
results,
type=c("perc", "bca")
)
ci_results
BOOTSTRAP CONFIDENCE INTERVAL CALCULATIONS
Based on 1000 bootstrap replicates
CALL :
boot.ci(boot.out = results, type = c("perc", "bca"))
Intervals :
Level Percentile BCa
95% ( 0.6753, 0.8835 ) ( 0.6344, 0.8561 )
Calculations and Intervals on Original Scale
Some BCa intervals may be unstable
ci_results$percent
conf
[1,] 0.95 25.03 975.98 0.6752993 0.8835035
ci_results$bca
conf
[1,] 0.95 3.77 896.91 0.6343659 0.8560896
多个统计量的自助法
返回回归系数向量的函数
bs <- function(formula, data, indices) {
d <- data[indices,]
fit <- lm(formula, data=d)
return(coef(fit))
}
自助抽样
set.seed(1234)
results <- boot(
data=mtcars,
statistic=bs,
R=1000,
formula=mpg ~ wt + disp
)
print(results)
ORDINARY NONPARAMETRIC BOOTSTRAP
Call:
boot(data = mtcars, statistic = bs, R = 1000, formula = mpg ~
wt + disp)
Bootstrap Statistics :
original bias std. error
t1* 34.96055404 4.715497e-02 2.546106756
t2* -3.35082533 -4.908125e-02 1.154800744
t3* -0.01772474 6.230927e-05 0.008518022
多个统计量使用索引
plot(
results,
index=2
)
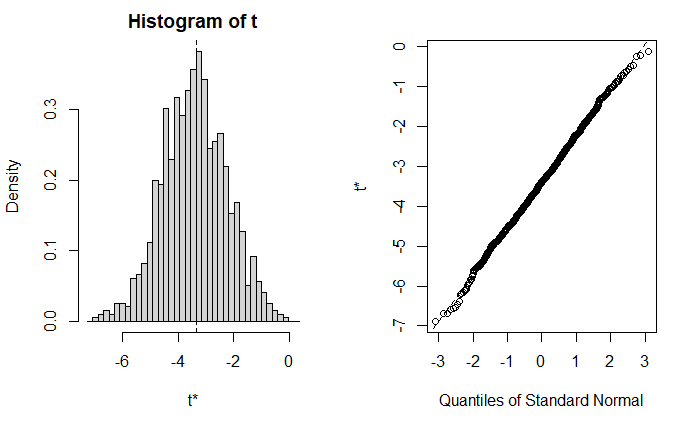
置信区间
boot.ci(
results,
type="bca",
index=2
)
BOOTSTRAP CONFIDENCE INTERVAL CALCULATIONS
Based on 1000 bootstrap replicates
CALL :
boot.ci(boot.out = results, type = "bca", index = 2)
Intervals :
Level BCa
95% (-5.477, -0.937 )
Calculations and Intervals on Original Scale
boot.ci(
results,
type="bca",
index=3
)
BOOTSTRAP CONFIDENCE INTERVAL CALCULATIONS
Based on 1000 bootstrap replicates
CALL :
boot.ci(boot.out = results, type = "bca", index = 3)
Intervals :
Level BCa
95% (-0.0334, -0.0011 )
Calculations and Intervals on Original Scale
参考
https://github.com/perillaroc/r-in-action-study
R 语言实战
