R语言实战:广义线性模型
本文内容来自《R 语言实战》(R in Action, 2nd),有部分修改
广义线性模型和 glm() 函数
标准线性模型:假设 Y 呈正态分布
广义线性模型:假设 Y 服从指数分布族中的一种分布
glm() 函数
基本形式
glm(
formula,
family=family(link=function),
data=data
)
Logistic 回归:用于二值响应变量 (0 和 1)
$$ log_{e}(\frac{\pi}{1-\pi}) = \beta_0 + \sum_{j=1}^{p}\beta_{j}X_{j} $$
glm(
Y ~ X1 + X2 + X3,
family=binomial(link="logit"),
data=mydata
)
泊松回归:适用于在给定时间内响应变量为事件发生数目的情形
$$ log_{e}(\lambda) = \beta_0 + \sum_{j=1}^{p}\beta_{j}X_{j} $$
glm(
Y ~ X1 + X2 + X3,
family=possion(link="log"),
data=mydata
)
标准线性回归:广义线性回归的一种特例
$$ \mu_{Y} = \beta_0 + \sum_{j=1}^{p}\beta_{j}X_{j} $$
glm(
Y ~ X1 + X2 + X3,
family=guassian(link="identity"),
data=mydata
)
与下面代码相同
lm(
Y ~ X1 + X2 + X3,
data=mydata
)
连用的函数
summary()coefficients()confint()residuals()anova()plot()predict()deviance()df.residual()
模型拟合和回归诊断
预测值与残差
plot(
predict(model, type="response"),
residuals(model, type="deviance")
)
帽子值
plot(hatvalues(model))
学生化残差
plot(rstudent(model))
Cook 距离统计量
plot(cooks.distance(model))
car 包的影像图
library(car)
influencePlot(model)
Logistic 回归
data(Affairs, package="AER")
head(Affairs)
affairs gender age yearsmarried children religiousness education
4 0 male 37 10.00 no 3 18
5 0 female 27 4.00 no 4 14
11 0 female 32 15.00 yes 1 12
16 0 male 57 15.00 yes 5 18
23 0 male 22 0.75 no 2 17
29 0 female 32 1.50 no 2 17
occupation rating ynaffair
4 7 4 No
5 6 4 No
11 1 4 No
16 6 5 No
23 6 3 No
29 5 5 No
summary(Affairs)
affairs gender age yearsmarried children
Min. : 0.000 female:315 Min. :17.50 Min. : 0.125 no :171
1st Qu.: 0.000 male :286 1st Qu.:27.00 1st Qu.: 4.000 yes:430
Median : 0.000 Median :32.00 Median : 7.000
Mean : 1.456 Mean :32.49 Mean : 8.178
3rd Qu.: 0.000 3rd Qu.:37.00 3rd Qu.:15.000
Max. :12.000 Max. :57.00 Max. :15.000
religiousness education occupation rating
Min. :1.000 Min. : 9.00 Min. :1.000 Min. :1.000
1st Qu.:2.000 1st Qu.:14.00 1st Qu.:3.000 1st Qu.:3.000
Median :3.000 Median :16.00 Median :5.000 Median :4.000
Mean :3.116 Mean :16.17 Mean :4.195 Mean :3.932
3rd Qu.:4.000 3rd Qu.:18.00 3rd Qu.:6.000 3rd Qu.:5.000
Max. :5.000 Max. :20.00 Max. :7.000 Max. :5.000
ynaffair
No :451
Yes:150
table(Affairs$affairs)
0 1 2 3 7 12
451 34 17 19 42 38
生成二值型变量
Affairs$ynaffair <- ifelse(
Affairs$affairs == 0, 0, 1
)
Affairs$ynaffair <- factor(
Affairs$ynaffair,
levels=c(0, 1),
labels=c("No", "Yes")
)
table(Affairs$ynaffair)
No Yes
451 150
使用 Logistic 回归拟合
fit_full <- glm(
ynaffair ~ gender + age + yearsmarried + children +
religiousness + education + occupation + rating,
data=Affairs,
family=binomial()
)
summary(fit_full)
Call:
glm(formula = ynaffair ~ gender + age + yearsmarried + children +
religiousness + education + occupation + rating, family = binomial(),
data = Affairs)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.5713 -0.7499 -0.5690 -0.2539 2.5191
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.37726 0.88776 1.551 0.120807
gendermale 0.28029 0.23909 1.172 0.241083
age -0.04426 0.01825 -2.425 0.015301 *
yearsmarried 0.09477 0.03221 2.942 0.003262 **
childrenyes 0.39767 0.29151 1.364 0.172508
religiousness -0.32472 0.08975 -3.618 0.000297 ***
education 0.02105 0.05051 0.417 0.676851
occupation 0.03092 0.07178 0.431 0.666630
rating -0.46845 0.09091 -5.153 2.56e-07 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 675.38 on 600 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 609.51 on 592 degrees of freedom
AIC: 627.51
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 4
去掉不显著的变量,重新拟合
fit_reduced <- glm(
ynaffair ~ age + yearsmarried + religiousness + rating,
data=Affairs,
family=binomial()
)
summary(fit_reduced)
Call:
glm(formula = ynaffair ~ age + yearsmarried + religiousness +
rating, family = binomial(), data = Affairs)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.6278 -0.7550 -0.5701 -0.2624 2.3998
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.93083 0.61032 3.164 0.001558 **
age -0.03527 0.01736 -2.032 0.042127 *
yearsmarried 0.10062 0.02921 3.445 0.000571 ***
religiousness -0.32902 0.08945 -3.678 0.000235 ***
rating -0.46136 0.08884 -5.193 2.06e-07 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 675.38 on 600 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 615.36 on 596 degrees of freedom
AIC: 625.36
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 4
使用卡方检验比较两个模型的效果是否相同
anova(
fit_reduced,
fit_full,
test="Chisq"
)
Analysis of Deviance Table
Model 1: ynaffair ~ age + yearsmarried + religiousness + rating
Model 2: ynaffair ~ gender + age + yearsmarried + children + religiousness +
education + occupation + rating
Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
1 596 615.36
2 592 609.51 4 5.8474 0.2108
卡方值不显著,说明两个模型预测效果相同,可以用变量较少的模型代替变量较多的模型
诊断图
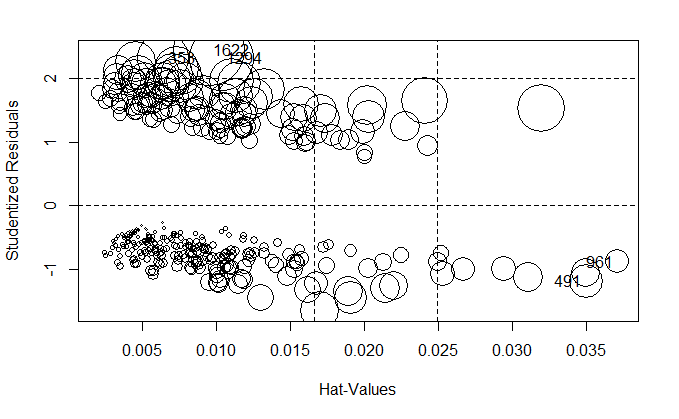
influencePlot(fit_reduced)
StudRes Hat CookD
491 -1.184602 0.035017325 0.007381522
961 -0.878964 0.037140782 0.003674050
353 2.314756 0.006420789 0.016875451
1294 2.308549 0.010371085 0.026380976
1622 2.433243 0.009515004 0.032601703
解释模型参数
回归系数
coefficients(fit_reduced)
(Intercept) age yearsmarried religiousness rating
1.93083017 -0.03527112 0.10062274 -0.32902386 -0.46136144
exp(coef(fit_reduced))
(Intercept) age yearsmarried religiousness rating
6.8952321 0.9653437 1.1058594 0.7196258 0.6304248
系数的置信区间
confint(fit_reduced)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 0.75404303 3.150622807
age -0.07006400 -0.001854759
yearsmarried 0.04388142 0.158562400
religiousness -0.50637196 -0.155156981
rating -0.63741235 -0.288566411
exp(confint(fit_reduced))
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 2.1255764 23.3506030
age 0.9323342 0.9981470
yearsmarried 1.0448584 1.1718250
religiousness 0.6026782 0.8562807
rating 0.5286586 0.7493370
评价预测变量对结果概率的影响
创建一个虚拟数据集,只有婚姻评分不同
test_data <- data.frame(
rating=1:5,
age=mean(Affairs$age),
yearsmarried=mean(Affairs$yearsmarried),
religiousness=mean(Affairs$religiousness)
)
test_data
rating age yearsmarried religiousness
1 1 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473
2 2 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473
3 3 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473
4 4 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473
5 5 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473
test_data$prob <- predict(
fit_reduced,
newdata=test_data,
type="response"
)
test_data
rating age yearsmarried religiousness prob
1 1 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473 0.5302296
2 2 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473 0.4157377
3 3 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473 0.3096712
4 4 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473 0.2204547
5 5 32.48752 8.177696 3.116473 0.1513079
年龄不同的虚拟数据集
test_data <- data.frame(
rating=mean(Affairs$rating),
age=seq(17, 57, 10),
yearsmarried=mean(Affairs$yearsmarried),
religiousness=mean(Affairs$religiousness)
)
test_data
rating age yearsmarried religiousness
1 3.93178 17 8.177696 3.116473
2 3.93178 27 8.177696 3.116473
3 3.93178 37 8.177696 3.116473
4 3.93178 47 8.177696 3.116473
5 3.93178 57 8.177696 3.116473
test_data$prob <- predict(
fit_reduced,
newdata=test_data,
type="response"
)
test_data
rating age yearsmarried religiousness prob
1 3.93178 17 8.177696 3.116473 0.3350834
2 3.93178 27 8.177696 3.116473 0.2615373
3 3.93178 37 8.177696 3.116473 0.1992953
4 3.93178 47 8.177696 3.116473 0.1488796
5 3.93178 57 8.177696 3.116473 0.1094738
过度离势
观测到的响应变量的方差大于期望的二项分布的方差。
检测方法1:二项分布模型的残差偏差除以残差自由度,如果比值比 1 大很多,可认为存在过度离势。
deviance(fit_reduced) / df.residual(fit_reduced)
[1] 1.03248
检测方法2:检验过度离势,需要拟合两次模型
fit <- glm(
ynaffair ~ age + yearsmarried + religiousness + rating,
data=Affairs,
family=binomial()
)
fit_od <- glm(
ynaffair ~ age + yearsmarried + religiousness + rating,
data=Affairs,
family=quasibinomial()
)
pchisq(
summary(fit_od)$dispersion * fit$df.residual,
fit$df.residual,
lower=FALSE
)
[1] 0.340122
不显著,说明不存在过度离势
扩展
稳健 Logistic 回归
robust 包的 glmRob() 函数
多项分布回归
mlogit 包中的 mlogit() 函数
序数 Logistic 回归
rms 包中的 lrm() 函数
泊松回归
robust 包中的 breslow.dat 数据集
data(breslow.dat, package="robust")
head(breslow.dat)
ID Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Base Age Trt Ysum sumY Age10 Base4
1 104 5 3 3 3 11 31 placebo 14 14 3.1 2.75
2 106 3 5 3 3 11 30 placebo 14 14 3.0 2.75
3 107 2 4 0 5 6 25 placebo 11 11 2.5 1.50
4 114 4 4 1 4 8 36 placebo 13 13 3.6 2.00
5 116 7 18 9 21 66 22 placebo 55 55 2.2 16.50
6 118 5 2 8 7 27 29 placebo 22 22 2.9 6.75
summary(breslow.dat[c(6, 7, 8, 10)])
Base Age Trt sumY
Min. : 6.00 Min. :18.00 placebo :28 Min. : 0.00
1st Qu.: 12.00 1st Qu.:23.00 progabide:31 1st Qu.: 11.50
Median : 22.00 Median :28.00 Median : 16.00
Mean : 31.22 Mean :28.34 Mean : 33.05
3rd Qu.: 41.00 3rd Qu.:32.00 3rd Qu.: 36.00
Max. :151.00 Max. :42.00 Max. :302.00
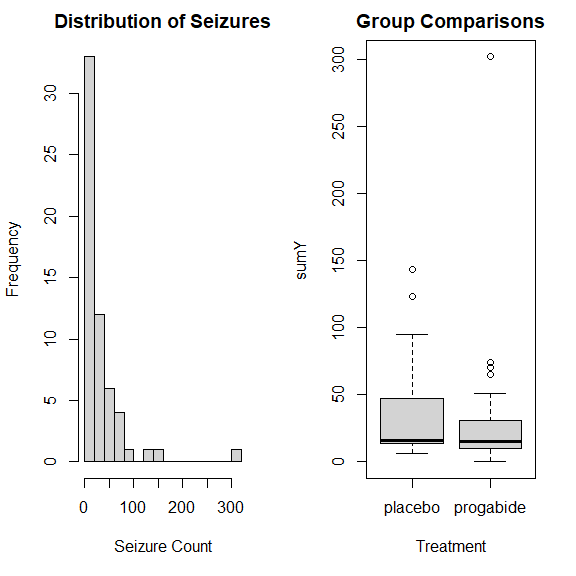
绘图分析
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1, 2))
with(
breslow.dat,
{
hist(
sumY,
breaks=20,
xlab="Seizure Count",
main="Distribution of Seizures"
)
boxplot(
sumY ~ Trt,
xlab="Treatment",
main="Group Comparisons"
)
}
)
par(opar)
泊松回归
fit <- glm(
sumY ~ Base + Age + Trt,
data=breslow.dat,
family=poisson()
)
summary(fit)
Call:
glm(formula = sumY ~ Base + Age + Trt, family = poisson(), data = breslow.dat)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-6.0569 -2.0433 -0.9397 0.7929 11.0061
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.9488259 0.1356191 14.370 < 2e-16 ***
Base 0.0226517 0.0005093 44.476 < 2e-16 ***
Age 0.0227401 0.0040240 5.651 1.59e-08 ***
Trtprogabide -0.1527009 0.0478051 -3.194 0.0014 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Dispersion parameter for poisson family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 2122.73 on 58 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 559.44 on 55 degrees of freedom
AIC: 850.71
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
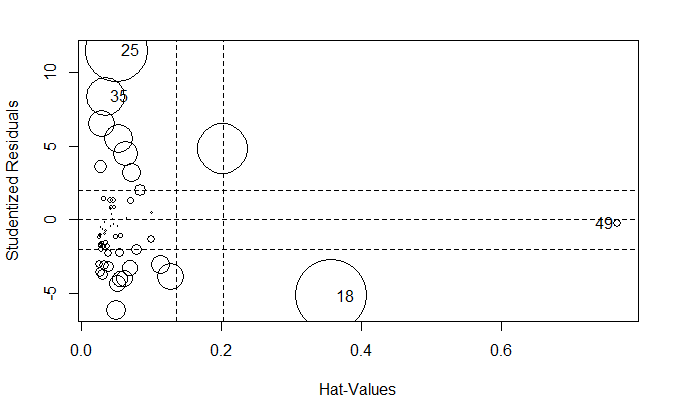
诊断图
influencePlot(fit)
解释模型参数
coef(fit)
(Intercept) Base Age Trtprogabide
1.94882593 0.02265174 0.02274013 -0.15270095
summary(fit)$coefficients
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.94882593 0.1356191170 14.369847 8.000803e-47
Base 0.02265174 0.0005093011 44.476125 0.000000e+00
Age 0.02274013 0.0040239969 5.651131 1.593953e-08
Trtprogabide -0.15270095 0.0478051047 -3.194239 1.401998e-03
exp(coef(fit))
(Intercept) Base Age Trtprogabide
7.0204403 1.0229102 1.0230007 0.8583864
过度离势
残差偏差 / 残差自由度
deviance(fit) / df.residual(fit)
[1] 10.1717
结果远大于 1,表明存在过度离势
qcc 包的 qcc.overdispersion.test() 函数检验泊松模型是否存在过度离势
library(qcc)
qcc.overdispersion.test(breslow.dat$sumY, type="poisson")
Overdispersion test Obs.Var/Theor.Var Statistic p-value
poisson data 62.87013 3646.468 0
p 值小于 0.05,表明存在过度离势
类泊松方法
fit_od <- glm(
sumY ~ Base + Age + Trt,
data=breslow.dat,
family=quasipoisson()
)
summary(fit_od)
Call:
glm(formula = sumY ~ Base + Age + Trt, family = quasipoisson(),
data = breslow.dat)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-6.0569 -2.0433 -0.9397 0.7929 11.0061
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 1.948826 0.465091 4.190 0.000102 ***
Base 0.022652 0.001747 12.969 < 2e-16 ***
Age 0.022740 0.013800 1.648 0.105085
Trtprogabide -0.152701 0.163943 -0.931 0.355702
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Dispersion parameter for quasipoisson family taken to be 11.76075)
Null deviance: 2122.73 on 58 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 559.44 on 55 degrees of freedom
AIC: NA
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
扩展
时间段变化的泊松回归
使用 glm() 中的 offset 选项
零膨胀的泊松回归
pscl 包中的 zeroinfl() 函数
稳健泊松回归
robust 包中的 glmRob() 函数
参考
https://github.com/perillaroc/r-in-action-study
R 语言实战
